Stock trading and foreign exchange, or “forex” trading, are similar in that they depend on taking advantage of constantly changing prices – but that’s where the similarities largely end. Understanding the differences between forex and stock trading can help you to decide whether one type of trading may be more suitable to your goals and style as a trader than the other. In this article, we’ll cover the basics of forex trading and detail the many ways in which it differs from equities trading.
Stock Trading and Forex Trading
Stock trading involves buying and selling shares of individual companies, whereas forex trading involves exchanging – buying and selling simultaneously – cash minted by two different countries. This means that the mechanisms underlying these two forms of trading are very different and can be advantageous under different situations. Stock trading is best when markets are rising, since low liquidity makes it difficult to short sell in falling markets. Forex trading, on the other hand, can be lucrative in any scenario since every trade involves both buying and selling and liquidity is high.
Similarities between Forex and Stocks
Although forex and stock trading are marked mostly by their differences, they do share some characteristics in common. Both forex and stock trading involve taking advantage of short-term shifts in prices to generate profit, and in the process entail risk that the stock or currency you are holding will fall-HANNA in value from the purchase price rather than rise. In addition, much like stock trading, forex traders rely heavily on technical analysis in order to identify probably price movements and inform trading behavior. Finally, trading both forex and stocks requires a strong fundamental understanding of how markets work and practice in order to turn a consistent profit.
Differences between Forex and Stocks
Regulation
One of the obvious differences between stock trading and forex trading is that they are regulated by different agencies within the US. Whereas the Securities and Exchange oversees all equities and stock options trading, forex trading comes under the purview of the Commodities Futures Trading Commission – a government agency – and the non-profit National Futures Association. One of the main goals of these regulatory is are to protect individual traders and investors from fraudulent brokers, which are abundant in the forex markets of less heavily regulated countries.
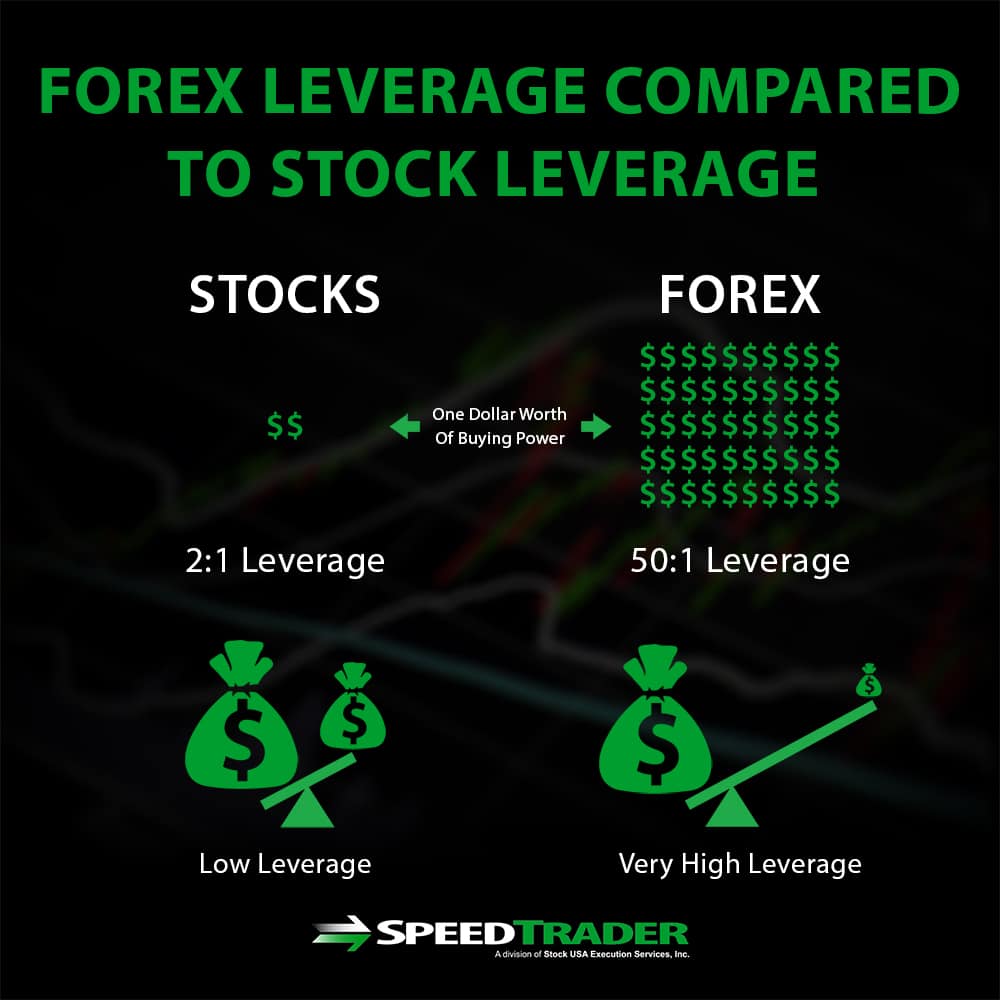
Leverage
The amount of leverage available in forex trading is overwhelming compared to that in stock trading, which can make forex trading both incredibly lucrative and also incredibly risky. In the US, forex trading typically operates at a 50:1 leverage, meaning that traders need to have only 2% of the value of the foreign currency they are trading available in their brokerage account. This is in contrast to the 2:1 leverage common amongst stock brokers, where traders must have 50% of the value of the stocks they are trading available as cash in their account.
Trading Hours
Forex trading is conducted 24 hours a day, in contrast to stock trading that operates on a much more limited timeframe and only during weekdays. Part of the reason for this is that forex trading does not rely on any central exchange with a physical location, but rather occurs globally over electronic communications networks. It is also critical for global trade that forex trading take place 24 hours a day since foreign currencies are in constant demand around the world. Stocks and other securities are not typically in demand enough after business hours in the country in which the companies underlying those stock reside, making it difficult to justify keeping the market open past business hours.
Volatility
In general, the stock market tends to be more volatile than the forex market since currencies tend to be relatively stable in price with respect to one another when economic conditions are steady. However, this is not always the case, and forex trading has a reputation for periods of extreme volatility – which may or may not coincide with periods of extreme volatility in national stock markets.
Market Size
While stocks may be traded globally, the market for equities is largely national rather than international. Forex, on the other hand, operates on a global market. This is aided by the fact that forex trading occurs 24 hours a day, so that it is possible for forex traders to trader across any currency depending on the time of day and what brokers are active. On the other hand, while there are typically thousands of stocks to choose from on a single exchange, forex trading revolves largely around 18 pairs of currencies that have particularly high liquidity.
Liquidity
Compared to stocks, forex is highly and consistently liquid. The reason for this is that stocks are limited in supply to a greater or lesser extent since they represent shares of a company. Blue chip stocks typically have many shares available and thus have high liquidity, while penny stocks typically have a low number of available shares and thus have low liquidity. On the other hand, while currencies are finite in supply, they are essentially infinite for the purposes of trading under normal economic conditions.
Catalysts and Price Influencers
The types of news that influences the prices of forex and stocks also differ somewhat. Forex prices are predominantly shifted by global news, whereas stock prices are most often responding to news about the company underlying the stock or its respective sector. Both forex and stock prices may respond to news about large-scale shifts in economic conditions within a country or to political news that traders believe will have an impact on the economy in the near future.
Which is Better for You?
Whether stock trading or forex trading is better for you largely depends on your goals as a trader, on your trading style, and on your tolerance for risk. Forex trading involves far more leverage and far less regulation than stock trading, which makes it both highly lucrative and highly risky. On the other hand, tracking forex market is often easier than tracking stock markets since there are only 18 common pairs of currencies to trade rather than thousands of potential stocks. One unusual drawback to forex trading compared to stock trading is that it takes place 24 hours a day, which means that you may need to be working at odd hours to realize certain trades and that the market is still changing whenever you are not working. Ultimately, practicing both forex trading and stock trading to find which form of trading fits you better is the best way to choose between them.
Conclusion
Forex and stock trading are highly divergent forms of trading based on short-term price action. Forex and stock trading differ in terms of the regulations surrounding trades, the size of the markets and hours of trading, the liquidity and volatility of prices, and even the types of news that prices respond to. Understanding both forex and stock trading can help you determine which type of trading better fits your goals and trading style.