Broad economic factors routinely have a jolting influence on the stock market, forcing traders to react both quickly and over time to adjust to new market conditions. Understanding the types of economic factors that affect the market and how they influence it can go a long way toward improving your profitability as a trader.
Why Traders Should Care
While some traders might find economic announcements and global news inherently interesting, there are a variety of reasons why every trader – from day traders to long-term investors – should pay attention to the economic factors that impact the stock market.
First, the more you understand about the economy, the more likely you are to succeed as a trader. Economic factors are in many cases the large-scale drivers of the stock market’s fortunes, whether in specific sectors or across the market as a whole. Recognizing the economic forces at play over both the short- and long-terms can help you hone your trading strategy and set positions that ride the larger economic current rather than fight it.
Even day traders who don’t hold positions overnight should pay attention to economic factors. Announcements about interest rate changes or the release of reports about job and wage growth can cause large, sudden intra-day shifts in the way the markets are trading. At the same time, sustained economic movements can dramatically affect the way that the markets are trading from day to day – for example, economic factors may influence whether the stock market is highly volatile or trending strongly.
Economic Factors
Interest Rates
Interest rates are one of the most important sets of numbers across the entire economy, including the stock market. Interest rates are set by the Federal Reserve as a way to make borrowing money more or less expensive, and in the process keep currency inflation to within an established target rate.
Changes in interest rates affect the entire economy in myriad ways. When interest rates are high, it is more expensive for consumers and businesses alike to borrow money – which can cause people to think twice about buying a home or a car or to borrow money to hire more employees or purchase new equipment. On the other hand, low interest rates can make it easier for the economy to expand.
It may be unsurprising, then, that interest rates have a big affect on the stock market – after all, stocks’ values are ultimately tied to how profitable their underlying companies are, and profitability may be restricted when interest rates are high and consumers and businesses are buying less stuff. Thus, interest rate announcements by the Federal Reserve can cause huge swings in intra-day trading and can cause the stock market to trend strongly upward – in response to lowered interest rates – or downward – in response to raised interest rates – for months afterward.
Traders can keep an eye on interest rates by watching for announcements by the Federal Reserve. Typically, the Federal Reserve gives several days’ notice of any upcoming announcement, at which point rumors about potential changes will begin to circulate.
Inflation
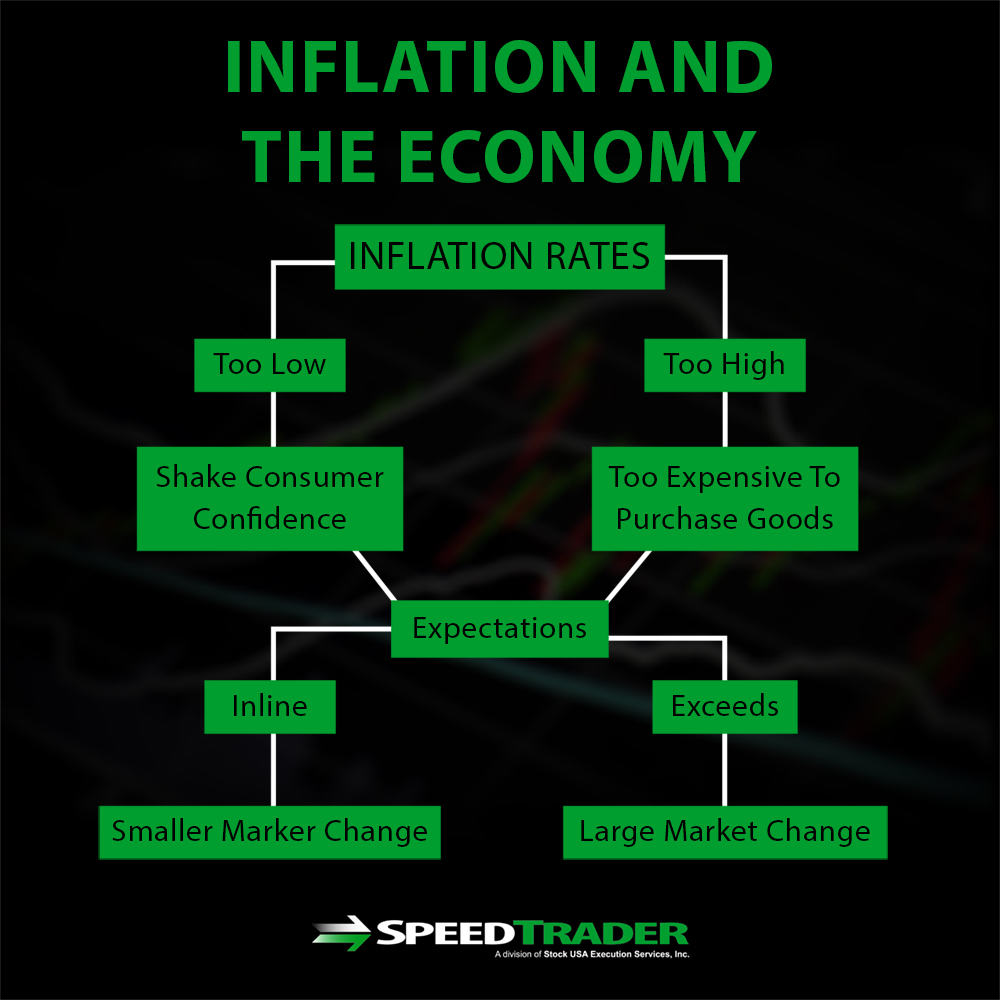
Inflation is the rate at which a currency devalues each year. For example, an inflation rate of 1% means that today’s $100 bill will only be worth the equivalent of $99 in one year’s time. While economists have some difficult pinning down the exact causes of inflation, raising interest rates is one of the best methods the Federal Reserve has to prevent inflation rates form skyrocketing.
Like interest rates, inflation rates have a number of effects on the economy that can be hard to tease apart. Interest rates that are too low can shake consumer confidence, which hurts businesses, while interest rates that are too high can make it too expensive for consumers to purchase goods. High inflation is particularly bad for businesses because it also devalues their monetary gains.
The stock market expects some small changes in inflation rates, so not every announcement of inflation rates will cause a market change if the announcement is in line with expectations. However, inflation announcements are typically negative for the market, both intra-day and potentially over a period of weeks or longer, if they greatly exceed the changes expected by investors.
Traders can track changes in inflation rate through the Bureau of Labor Statistic’s Consumer Price Index, which is released monthly.
Politics
Politics, both domestic and international, can have a large influence on the stock market.
In terms of domestic politics, this can best be seen when major elections – like the mid-term or presidential elections – occur. Typically, investors see one candidate as better than the other as offering better policies for increasing corporate and shareholder profits or for improving the overall economy, which can cause large multi-day spikes in the way the market is trending.
The US’s trade war with China is an example of how international politics can also dramatically affect the marketplace. Uncertainty about the economic ramifications of this political fight – which has specifically been fought with tariffs, which affect the price of good for consumers and businesses – has translated into volatility and negative price movements in the stock market.
Unlike interest or inflation rates, politics is not always overtly economic, which can make it difficult for traders to parse out what political news will have an impact on the market and what news will not. The best resources for following how politics may affect the stock market, and whether that impact will be positive or negative and short-lived or long-term, are often financial news outlets.
Foreign Markets
The health of foreign markets – in Europe, Asia, or elsewhere – can sometimes, but not always, have an impact on US markets.
The main determinant of whether foreign markets will affect US markets, and how dramatic that impact may be, is how dependent US corporations or consumers are on those foreign markets. In many cases, investors worry that crisis in one country or market may spread because of the global nature of the companies that make up the large US exchanges and the potential increase in the costs of foreign goods if a currency is destabilized. In other cases, such as has been the case when financial distress has hit China, investors worry that the growth of US companies will slow as their global marketplace becomes less valuable.
Still, it can be hard to predict how actions in foreign markets will generate a reaction in US markets. Typically, reactions from foreign market movements are short-lived – on the order of days to months – and will not affect long-term investors, although day traders and short-term investors will need to be wary of this economic factor. While it is possible for traders to monitor foreign stock exchanges just as they would US exchanges, financial news services are a more sustainable way to keep an eye on foreign stock activity that could impact the US.
Unemployment Rate & Jobs Reports
The relationship between unemployment rates and the stock market can be complex. While it might intuitively seem as if lower unemployment is good for the economy and therefor must be associated with a bullish stock market, that is not always the case. Instead, when unemployment is low, investors tend to be more willing to pay high price-to-earnings ratios for companies, which can turn bearish since high valuations are associated with below average forward returns.
That’s not to say that high unemployment is good for the stock market, either. High unemployment typically signals that the economy is in trouble and that consumers and businesses are not likely to spend money, which is bad for corporations across the board. Thus, like for inflation rates, there is a sweet spot when it comes to matching unemployment rates to stock market outlook.
Unemployment rates are typically announced monthly by the Bureau of Labor Statistics in what have become known as jobs reports. These reports can cause wild intra-day swings in the stock market, even when there is little news or it is difficult to interpret the jobs report’s findings in the context of what it means for the broader economy. In addition, jobs reports can give investors comfort or make them wary, which can influence longer-scale changes in the stock market.
Economic Growth & Projections
Reports of economic growth and projections of future growth are a frequent trigger for intra-day and multi-day swings in the stock market. In the same way that corporations need to perform on both reported profits and projected profits during earnings reports, economic growth announcements typically need to meet investor’s expectations of both current and future growth in order to cause a significant uptick in stock prices. While disappointing economic outlook reports may not have much of an effect in a bullish market, they can have a significant effect in volatile or bearish market conditions.
Like jobs reports, economic growth reports can be difficult to interpret in the context of the both the economy as a whole and the stock market. However, investor sentiment is usually clear soon after the report’s release and the effect can be intra-day or sustained over a period of days to weeks.
Economic growth reports are typically released quarterly by the Bureau of Economic Analysis.
Conclusion
The stock market is one part of the overall economy, but it does not stand alone from the rest of the economy. A variety of economic factors, including interest and inflation rates, overall economic growth, unemployment, and even politics, can influence the stock market on both intra-day and longer timescales. Smart investors need to be aware of what economic factors can impact the stock market, when and where changes in these factors are announced, and how to trade around them.